[Codeforces] 1475D. Cleaning the Phone explained

Problem
Approach
It’s “Two pointers”.
First, divide \(a_i\) into two separate arrays based on convenience point and sort them in descending order.
We call those arrays one and two, respectively.
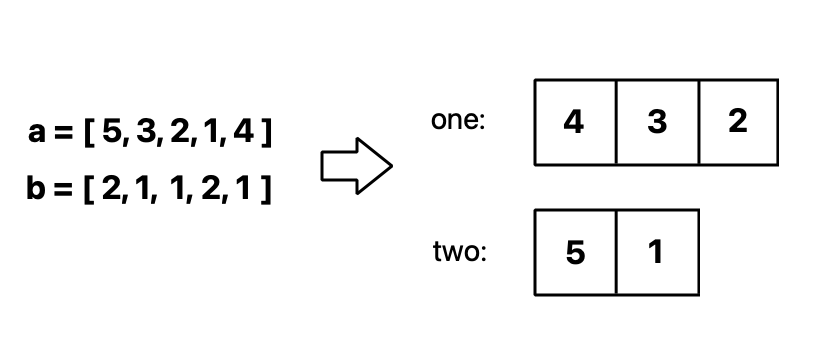
Say we pick l apps from one, and r apps from two.
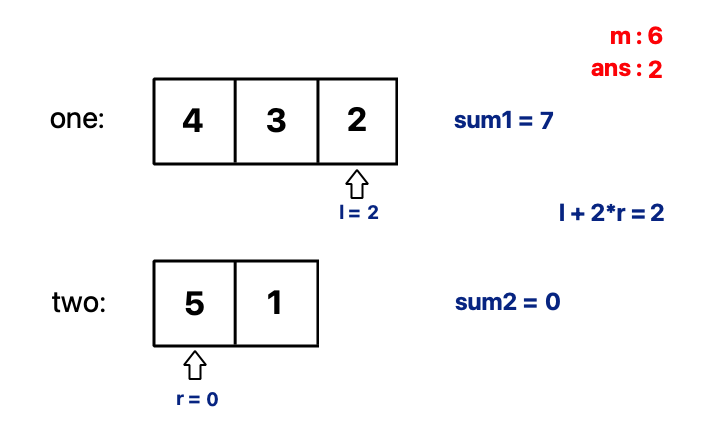
We start by
l= 0r= two.size()
When we exclude apps that we already decided to delete(r apps), we greedily pick small sized apps first.
On the other hand, we pick big size apps first when we add new ones.
At first, the sum of memories are sum1 = 0, sum2 = 6, respectively.
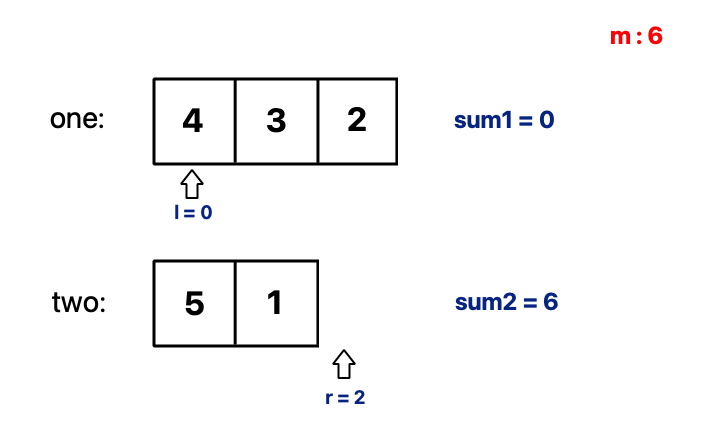
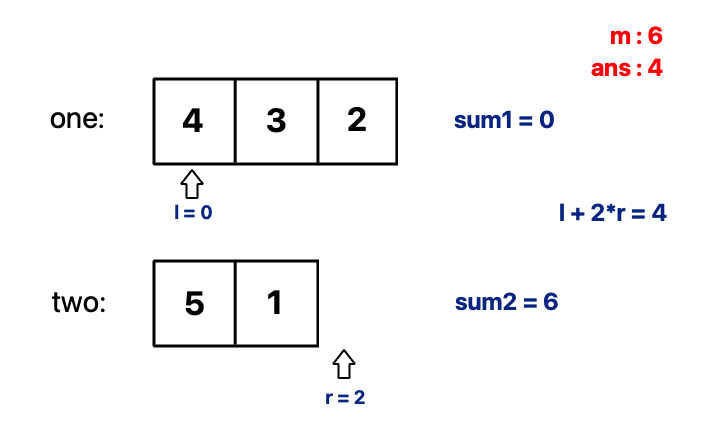
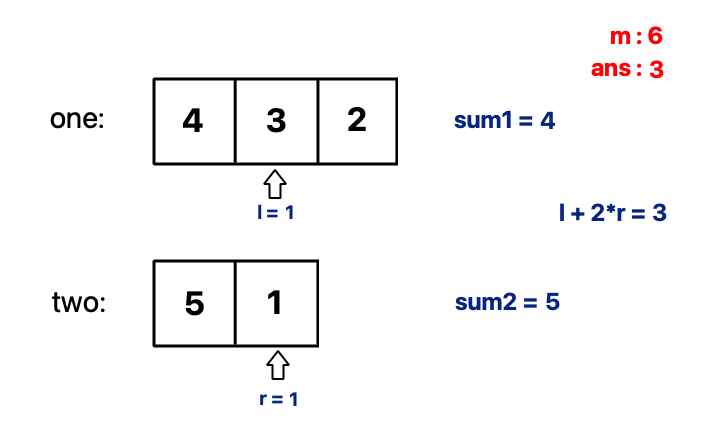
Now, for l = 0, 1, … one.size() do:
- \(sum2 = sum2 - two[r-1]\) and decrement
runtil \(sum1 + sum2 >= m\) is satisfied. - answer = min(answer,
l+ 2*r) - \(sum1 = sum1 + one[l]\)
It takes \(O(n\log{n})\) for sorting and \(O(n)\) for iteration.
Code

/**
* written: 2022-03-17 20:26:37 Thu [KST]
* @jooncco's mac.
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define FAST_IO ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define f first
#define s second
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pll;
typedef vector<int> vi;
typedef vector<ll> vl;
typedef deque<int> di;
typedef deque<ll> dl;
typedef priority_queue<int, vi, less<int> > maxHeap;
typedef priority_queue<int, vi, greater<int> > minHeap;
const ll INF= 1e16;
int n,m;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
vi arr(n);
for (int &mem : arr) cin >> mem;
vi one, two;
int conv;
for (int i=0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> conv;
if (conv == 1) one.push_back(arr[i]);
if (conv == 2) two.push_back(arr[i]);
}
sort(one.rbegin(), one.rend());
sort(two.rbegin(), two.rend());
ll ans= INF;
ll sum1= 0, sum2= accumulate(two.begin(), two.end(), 0ll);
int r= two.size();
for (int l=0; l <= one.size(); ++l) {
while (r > 0 && sum1 + sum2 - two[r-1] >= m) {
sum2 -= two[--r];
}
if (r > -1 && sum1 + sum2 >= m) ans= min(ans, l+2ll*r);
if (l < one.size()) sum1 += one[l];
}
cout << (ans == INF ? -1 : ans) << "\n";
}
int main() {
FAST_IO;
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) solve();
}
Complexity
- Time: \(O(n\log{n} + n)\)
- Space: \(O(n)\)


Leave a comment