[LeetCode] 53. Maximum Subarray explained

Problem
Approach
Solution 1: DP
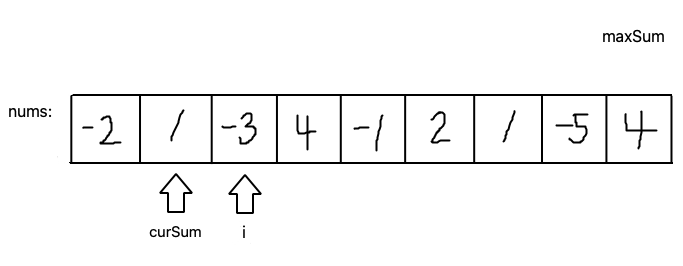
One pass from left to right.
While iterating the nums array, update curSum value with larger of those two.
- nums[i]
- curSum + nums[i]
The answer maxSum is the maximum value among all curSums.
Solution 2: Divide and conquer
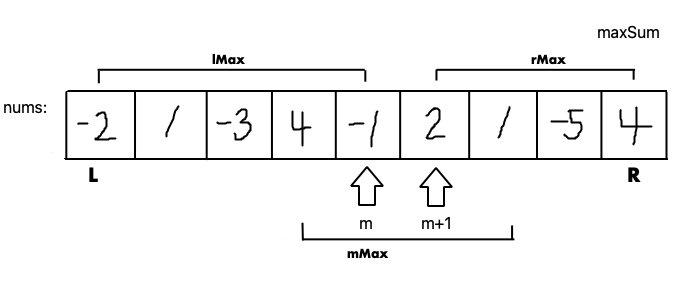
Think of the answer maxSum in a subarray nums[L:R]. It’s among those three.
- sum of subarray containing values
nums[m]andnums[m+1](mMax) maxSumin subarraynums[L:m](lMax)maxSumin subarraynums[m+1:R](rMax)
All we have to do is:
- calculate the mMax
- find
maxSumin left and right subarrays (recursive call) - return max among those three
Code
Solution 1: DP

typedef vector<int> vi;
class Solution {
private:
const int NEG_INF= -1e5;
public:
int maxSubArray(vi &nums) {
int n= nums.size(), ans= NEG_INF, curSum= NEG_INF;
for (int i=0; i < n; ++i) {
curSum= max(nums[i], curSum+nums[i]);
ans= max(ans, curSum);
}
return ans;
}
};
Solution 2: Divide and conquer
typedef vector<int> vi;
class Solution {
private:
int maxSum(vi &nums, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) return nums[L];
int m= L-(L-R)/2;
// calculate maxSubarray containing nums[m] to the left
int mMaxL= nums[m], lSum= nums[m];
for (int i=m-1; i >= L; --i) {
lSum += nums[i];
mMaxL= max(mMaxL, lSum);
}
// calculate maxSubarray containing nums[m+1] to the right
int mMaxR= nums[m+1], rSum= nums[m+1];
for (int i=m+2; i <= R; ++i) {
rSum += nums[i];
mMaxR= max(mMaxR, rSum);
}
int mMax= mMaxL+mMaxR;
return max( mMax, max( maxSum(nums, L, m), maxSum(nums, m+1, R) ) );
}
public:
int maxSubArray(vi &nums) {
int n= nums.size();
return maxSum(nums, 0, n-1);
}
};
Complexity
Solution 1
- Time: \(O(n)\)
- Space: \(O(1)\)
Solution 2
- Time: \(O(N{\log}N)\)
- Space: \(O(1)\)

Leave a comment